JBOX (english description): Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
| (12 dazwischenliegende Versionen von 2 Benutzern werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 4: | Zeile 4: | ||
JBOX creates parametrized boxes; essentially the wall parts of a box as CAD-file. | JBOX creates parametrized boxes; essentially the wall parts of a box as CAD-file. | ||
You simply define parameters like ''length, width, height etc.'', the rest does JBOX. | You simply define parameters like ''length, width, height etc.'', the rest does JBOX. | ||
| − | |||
JBOX needs Java 6 and runs on Windows, Linux and Mac. | JBOX needs Java 6 and runs on Windows, Linux and Mac. | ||
| − | Additionally you need QCAD. | + | Additionally you need QCAD or LibreCAD to open the output files and work with them. |
| − | + | (these are the programs which I used for testing) Now since version 2.0 the output dxf-files | |
| − | + | should open for any 2D-CAD-program. | |
| − | {{zip|JBOX.zip| | + | {{zip|JBOX.zip|292 KB|Version vom 16.2.2015}} |
(Sourcecode included) | (Sourcecode included) | ||
| Zeile 19: | Zeile 18: | ||
After download click on '''runJBOX.bat'''; it starts a Java-GUI where you define the parameters of your design. | After download click on '''runJBOX.bat'''; it starts a Java-GUI where you define the parameters of your design. | ||
For instance, for a standard box you define ''length, width, height, material thickness'' | For instance, for a standard box you define ''length, width, height, material thickness'' | ||
| − | and ''laser cutting''. After clicking the | + | and ''laser cutting''. After clicking the ''generate''-button (you have to define a dxf-file at this point) |
the design is generated into the chosen file. | the design is generated into the chosen file. | ||
After generating you have to open the file once with qcad and store it; this rectifies the file to a proper dxf. | After generating you have to open the file once with qcad and store it; this rectifies the file to a proper dxf. | ||
| Zeile 26: | Zeile 25: | ||
to material thickness) stärke). For extra wide teeth enter the desired value | to material thickness) stärke). For extra wide teeth enter the desired value | ||
in field ''zinkung length''. | in field ''zinkung length''. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Hints=== | ===Hints=== | ||
| Zeile 48: | Zeile 44: | ||
===Standard Box=== | ===Standard Box=== | ||
The standard box consisting of its six walls. | The standard box consisting of its six walls. | ||
| − | |||
===Recursive Drawers=== | ===Recursive Drawers=== | ||
| − | [[Image:Gehäuseschachtel.jpg|thumb|Box to contain and fix Arduino and | + | [[Image:Gehäuseschachtel.jpg|thumb|Box with raised floor to contain and fix Arduino and Pololu (Top and Bottom)]] |
With this option you can create ''Matryoshka'' boxes. I call them also the | With this option you can create ''Matryoshka'' boxes. I call them also the | ||
''recursive boxes'. | ''recursive boxes'. | ||
Additonal parameter is the number of drawer and the size of the hole | Additonal parameter is the number of drawer and the size of the hole | ||
to push the drawers out. | to push the drawers out. | ||
| − | |||
===Multidrawer=== | ===Multidrawer=== | ||
A multidrawer is a half open box with several drawers. | A multidrawer is a half open box with several drawers. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Box with raised floor=== | ===Box with raised floor=== | ||
| − | |||
A box where the bottom wall is raised. (raise height is a a parameter) | A box where the bottom wall is raised. (raise height is a a parameter) | ||
This design is meant as casing of electronic gadgets. | This design is meant as casing of electronic gadgets. | ||
| Zeile 70: | Zeile 60: | ||
The program generates parts which fit exactly together. | The program generates parts which fit exactly together. | ||
However, often the box you need will be a little different. | However, often the box you need will be a little different. | ||
| − | For instance for | + | For instance for an electronic casing you will put openings |
at various places. Or you want to have the edge contain the | at various places. Or you want to have the edge contain the | ||
teeth holes completely. | teeth holes completely. | ||
| Zeile 77: | Zeile 67: | ||
I have progammed like the box with the raised floor, but one could | I have progammed like the box with the raised floor, but one could | ||
do these adaptions from a standard box, manually, with little effort. | do these adaptions from a standard box, manually, with little effort. | ||
| − | |||
==Feedback== | ==Feedback== | ||
| − | You can | + | You can leave questions and suggestions at the discussion page of this arcticle. |
| − | |||
[[Category:Lasercutter]] [[Category:Projekte]] | [[Category:Lasercutter]] [[Category:Projekte]] | ||
Aktuelle Version vom 12. Jänner 2016, 10:43 Uhr
To read the German description go to JBOX
JBOX creates parametrized boxes; essentially the wall parts of a box as CAD-file. You simply define parameters like length, width, height etc., the rest does JBOX. JBOX needs Java 6 and runs on Windows, Linux and Mac. Additionally you need QCAD or LibreCAD to open the output files and work with them. (these are the programs which I used for testing) Now since version 2.0 the output dxf-files should open for any 2D-CAD-program.
(Sourcecode included)
HowTo
JBOX
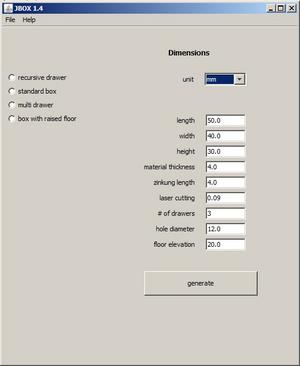
After download click on runJBOX.bat; it starts a Java-GUI where you define the parameters of your design. For instance, for a standard box you define length, width, height, material thickness and laser cutting. After clicking the generate-button (you have to define a dxf-file at this point) the design is generated into the chosen file. After generating you have to open the file once with qcad and store it; this rectifies the file to a proper dxf.
Additional parameter (since versin 1.4) is tooth width (default is a tooth width equal to material thickness) stärke). For extra wide teeth enter the desired value in field zinkung length.
Hints
The value for the paramter laser cutting is typically chosen between 0.03 und 0.2 millimeters. Wenn you choose a higher value the pieces will fit more tightly; an option when you want to work without glue. 0.2 millimeter is already an extreme value; for instance when you work with plywood you can hammer the wall pieces into place. The box will hold without glue.
The generated design is well suited to refine it manually in QCAD (or any CAD-program of your choice) For instance you will need extra holes when you work on a box for an electronic circuit.
Generally it is advisable to rearrange the generated parts (manually, in your CAD-program) to use your cutting material sparingly. When I have a large job of many pieces I generate one or several rectangles with the size of the raw sheets. Working with these rectangles you can make best use of your material almost up to the last millimeter.
Boxes
Standard Box
The standard box consisting of its six walls.
Recursive Drawers
With this option you can create Matryoshka boxes. I call them also the recursive boxes'. Additonal parameter is the number of drawer and the size of the hole to push the drawers out.
Multidrawer
A multidrawer is a half open box with several drawers.
Box with raised floor
A box where the bottom wall is raised. (raise height is a a parameter) This design is meant as casing of electronic gadgets. The raised box floor gives room to fix your nuts and hide them too.
Customized Boxes
The program generates parts which fit exactly together. However, often the box you need will be a little different. For instance for an electronic casing you will put openings at various places. Or you want to have the edge contain the teeth holes completely.
Use the result of JBOX as a building block to go on. Some of these changes I have progammed like the box with the raised floor, but one could do these adaptions from a standard box, manually, with little effort.
Feedback
You can leave questions and suggestions at the discussion page of this arcticle.